
MSP Corporation
M agnesium S aves our planet
A company aiming for a magnesium recycling society
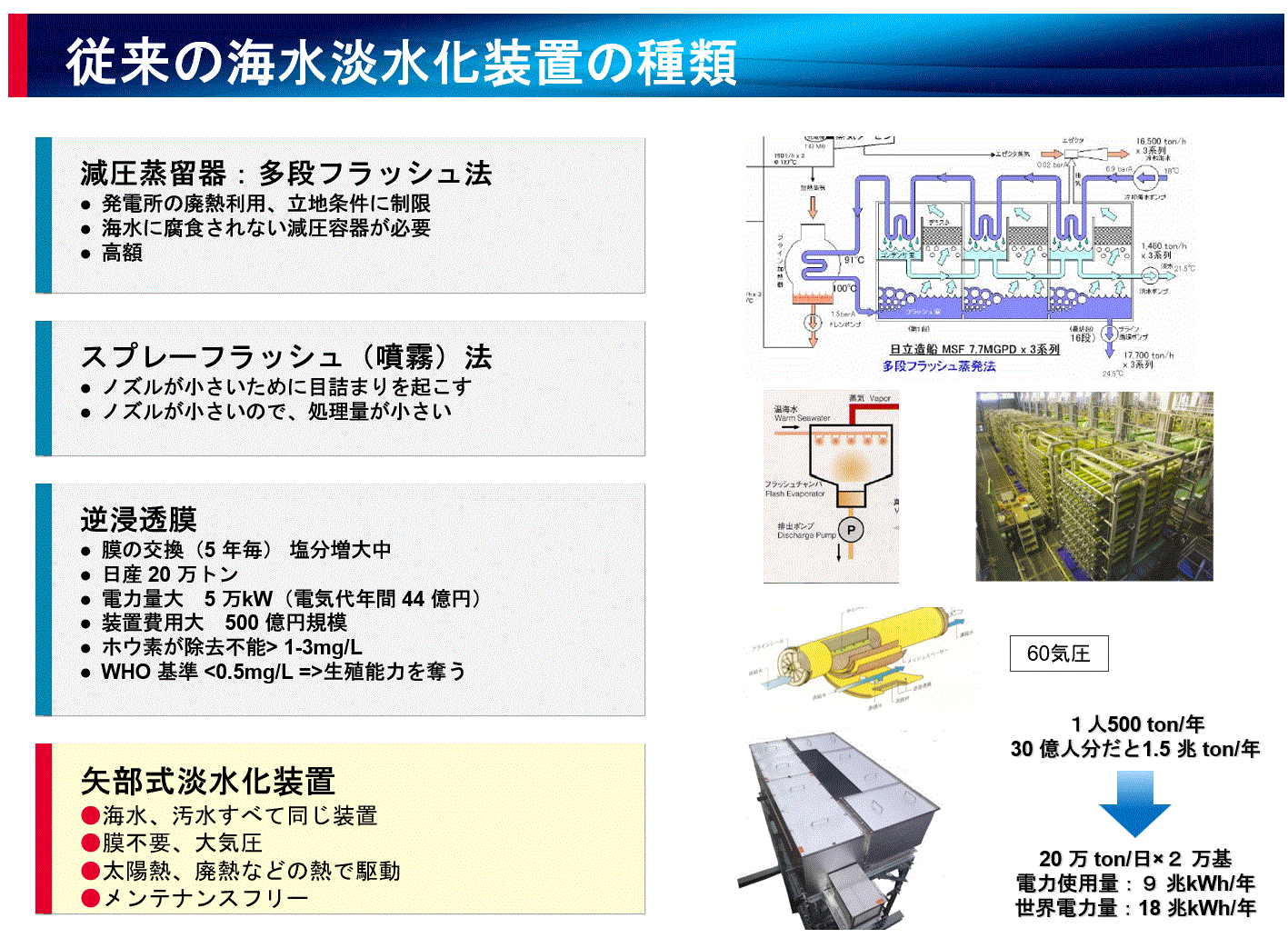
Seawater desalination device that extracts magnesium from seawater
There are 1800 trillion tons of magnesium (100,000 years worth of oil equivalent) in seawater around the world. How to get this out was a big issue. Previously, an electrolysis method was proposed, but it requires a huge amount of energy, so magnesium made in this way cannot be used in a decarbonized society. In addition, there are seawater desalination devices such as RO (reverse osmosis membrane) membranes, but these are for making drinking water from seawater, and are designed so that salt and magnesium are discarded as unnecessary. increase.
Professor Emeritus of Tokyo Institute of Technology Yabe proposed the world's first seawater desalination device specializing in magnesium sampling. Here's what this looks like.


Evaporation at atmospheric pressure
Many people misunderstand the difference between boiling and evaporation, but boiling is the phenomenon in which bubbles form inside the water when it reaches its boiling temperature (100 degrees Celsius at atmospheric pressure for water). On the other hand, evaporation is the phenomenon in which water molecules fly out from the surface, like steam from coffee, even if the water has not yet reached its boiling point.
Even if you sweat, even if your body temperature is around 30 degrees, the sweat dries. In other words, the sweat evaporates.

However, it takes more than several tens of minutes for sweat to dry. To speed this up, the surface area needs to be increased. As shown in the left figure, the surface area increases dramatically if water is made into tiny spheres. There are many methods for turning water into fine particles, such as applying ultrasonic vibrations or spraying water from tiny nozzles, but a simpler method is needed to combine this with heat recovery, which will be discussed later.
An ideal solution for this is the microbubble generator for fish farming proposed by Yabe in 1975. This simply involves directing water at a rapidly rotating water wheel.
This method made it possible to create a device that could evaporate at atmospheric pressure. This has the great advantage that the device can be made out of plastic, making it lightweight and inexpensive.


Experiment at a sewage treatment plant in Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
December 10, 2019

A portable sewage treatment device capable of producing 1 liter per hour was carried by baggage from Japan, and the experiment

Sewage (left) becomes purified water (right)

Support for existing equipment (remora plan)
Existing seawater desalination equipment such as reverse osmosis membranes dump seawater containing high concentrations of salt and impurities into the ocean.
Use Yabe's freshwater equipment to solve this problem. We will call this the remora project. This is because I don't have to do anything just by sticking to a huge shark called the reverse osmosis membrane method. In the reverse osmosis membrane method, 1 fresh water is produced and 2 high-concentration seawater is released with 3 seawater inputs. This is the cause of the problem, so if you put Yabe's device there, you can generate 2 fresh water from this 2 high-concentration seawater, and solve the pollution problem. This plan will solve the pollution problem of existing equipment and triple the amount of fresh water produced.

3 billion people will be short of water in 2025
Nikkei Science May 2001 issue


The RO (reverse osmosis membrane) method requires new electricity



